

release time:2024/07/29
Compared with round wire motors, flat wire motors have high slot filling rate, high power density, good NVH performance, good heat dissipation, and are easy to realize automated production. Its disadvantages are large AC loss, high process difficulty, and large equipment investment.
Among them, X-PIN motor can reduce the size of welding end wire package by 8-12mm.
But at the same time, there are the following process problems: head twisting control, head cutting, welding clamping, paint burning and other problems.
Design input stator slot type, copper wire gauge, connection diagram
3D feature recognition
Parameter assignment
Hairpin wire 3D modeling
Winding connection
Line shape optimization
Appearance design
Molding mold, determine the stator envelope size as integrated layout input
Thermal field, NVH simulation model input
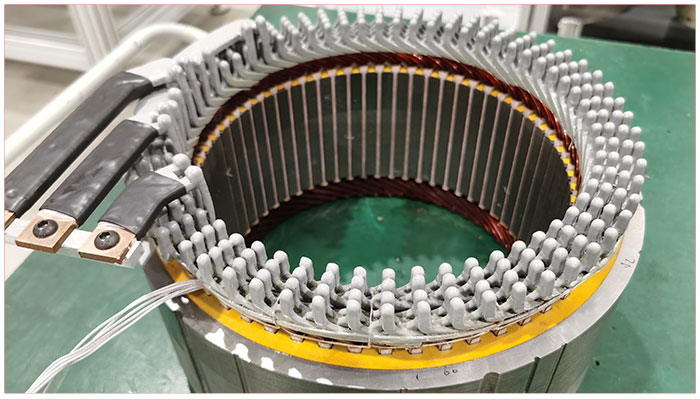
Core feeding
Paper insertion
Wire forming, wire insertion, copper wire transfer
Copper wire pressing
Flaring
Twist head
Cut flat tool installation
Cut flat
Connecting wire welding
Welding inspection
Repair welding
Remove cut flat tool installation
Welding
Repair welding
Remove tool installation
Thermistor installation
Electrical performance testing
Coating on line
Heating
Coating
Coating curing
Pre-paint insulation
Paint dripping
Paint dripping curing
Cooling off line
Appearance inspection
Three-wire copper busbar welding
Electrical performance testing
Laser marking
Dimensional appearance inspection
Cleaning
Finished product off line
Mechanical depainting: stamping, grinding, scraping
Process characteristics: fast cycle, clean depainting, poor flexibility, damage to copper wire, regular mold replacement.
Laser depainting:
Process characteristics: small damage to copper wire, good consistency, good flexibility, high equipment cost, attention should be paid to depainting residue and black edge problems.
Structural design and process thinking
Splitting and pulling forming: suitable for motors with large aspect ratio and few winding layers.
CNC forming: large equipment investment, high flexibility, convenient linear compensation, slow cycle.
Mold forming: stable linear size, simple equipment, fast cycle, easy to damage wire, poor flexibility.
Mixed forming: 2DCNC+3D mold
Manual wire insertion: manually insert the formed copper wire directly into the stator core in the prescribed order. Suitable for low requirements for line accuracy, low equipment investment, slow beat, uneven U-shaped ends, easy to insert the wrong wire, easy to damage the wire and paper.
Automatic wire insertion: Generally, the equipment automatically inserts the formed copper wire into the transfer wire cup, and then the equipment grabs the winding as a whole and inserts it into the stator core. Stable quality and fast beat. High requirements for line accuracy. High equipment investment and high process difficulty.
Semi-automatic wire insertion: Manually insert the formed copper wire into the transfer wire cup, and then the equipment grabs the winding as a whole and inserts it into the stator core.
Between manual and automatic, the process difficulty is moderate and widely used.
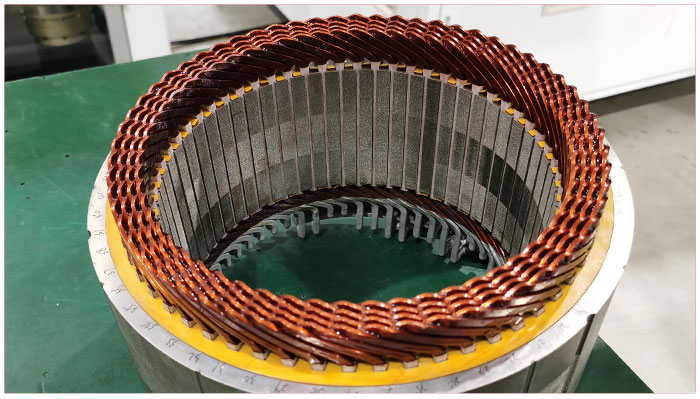
Classification: single-layer twisting, multi-layer twisting
Requirements: No biting or top wire. No explosion or cracking of the insulation paper. The position of the solder joints is accurate and neat. The size of the wire package meets the requirements.
Laser welding: stable quality and fast cycle. Small heat-affected zone. High requirements for joint position. Welding is prone to spatter. Large equipment investment.
Requirements: The welds are uniform, full and free of defects. The paint is intact and there is no spatter. The wire package size meets the requirements. The welds meet the requirements for pull-out force and penetration depth.
Ningbo Nide Mechanical Equipment Co., Ltd. focuses on providing customers with highly automated, information-based, intelligent, and flexible overall motor manufacturing solutions, focusing on stators, rotors and complete machine assembly lines for various motors. We have provided flat wire motor manufacturing solutions and round wire motor manufacturing solutions to many customers around the world, which are used in new energy vehicles, industry, home appliances, etc. Especially for round wire motor manufacturing lines, we have rich design experience and a professional technical team to provide customers with a series of automated motor manufacturing equipment such as motor stator manufacturing lines, rotor manufacturing lines, and motor assembly lines to meet customers' customized needs for motor manufacturing.
Copyright © Ningbo Nide Mechanical Equipment Co., Ltd.